Background Information
Ipomoeassin F is one of six ipomoeassins extracted from Ipomoea squamosa in the Suriname Rainforest1, 2. Many compounds derived from the Ipomoea genus contain glycoresins, meaning they have a sugar molecule and a long carbon chain1. Within the Ipomoea genus, there are many organisms of benefit to humans. Such as, Ipomoeas batatas the sweet potato, and Ipomoea leptophylla which is active against Mycobacterium tuberculosis to name a few1. Ipomoea squamosa are morning glories, a very common flower1. The original interest in the ipomoeassins stemmed from their potent activity against the M109 lung cancer cell line1. In the initial investigation, there were only five ipomoeassins (A-E) identified and they were determined to be active against the A2780 ovarian cancer cell line1.
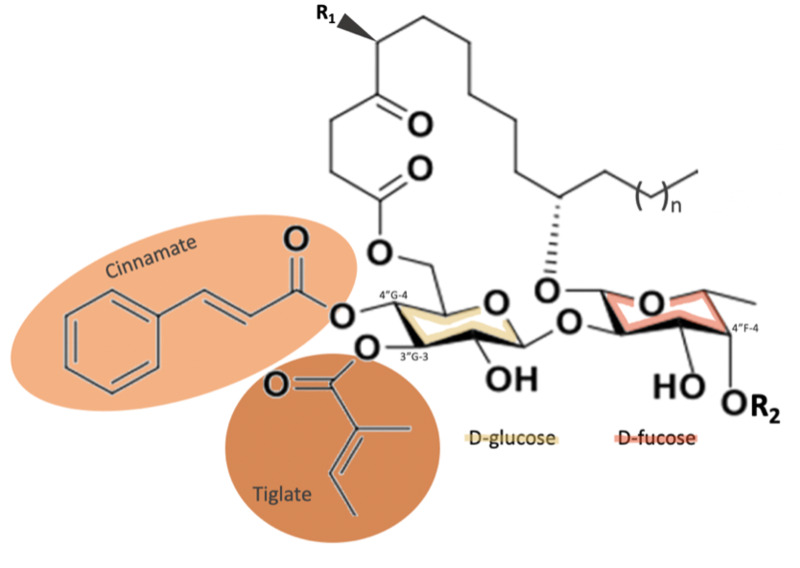
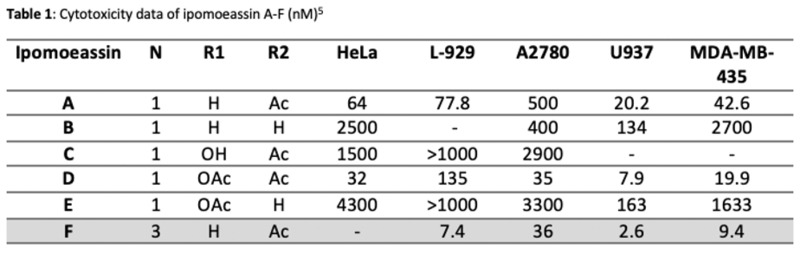
All of the ipomoeassins contain a D-glucose attached to a D-fucose via a B1-2 bond (Figure 1). A cinnamate moiety is connected to the glucose at C4 and a tiglate moiety at C3. The differences between the ipomoeassins comes down to what groups they have at R1 and R2 (Table 1).
Two years later Cao and associates re-investigated their separations from the previous study and discovered at sixth ipomoeassin2. Ipomoeassin F is very similar to ipomoeassin A, the only difference lies in the length of the fatty acid chain2. Ipomoeassin F has 16 carbons whereas A has 14 carbons2. Ipomoeassin F turned out to be over 10 times more cytotoxic than ipomoeassin A toward the A2780 human ovarian cancer cell line2. This discovery hinted that slight changes to the structure of ipomoeassin F can significantly increase the activity of the molecules against cancer cell lines2.
The IC50 values of all the ipomoeassins against various cancer cell lines were determined (Table 1). IC50 is the measure of how much of a given compound is needed to kill 50% of the cancer cells, meaning the lower the concentration the more active against the cancer cells. Ipomoeassin F displayed the most activity against the cancer cell lines.
In order to determine the mechanism of how ipomoeassin F interacts with a cell, an efficient synthesis is required. Thus far there have been three total syntheses to date. Fürstner’s group in 2009 with an overall yield of about 1.0%3. Postema’s group, also in 2009, with an overall yield of 0.4%4. And Shi’s group, in 2015, with an overall yield of around 3.8%5. A goal within our lab is to optimize the overall synthesis of ipomoeassin F by decreasing cost, labor, and time while increasing the yield.